Degree Costs and Financing are central to the pursuit of higher education, a journey that often comes with significant financial implications. Understanding the multifaceted costs involved, exploring diverse financing options, and implementing strategic management techniques are crucial steps for students and their families.
This guide delves into the intricacies of degree costs, providing insights into the factors that influence them and offering a comprehensive overview of financing options available to help mitigate the financial burden of higher education.
From tuition and fees to books and living expenses, the costs associated with pursuing a degree can vary widely depending on factors such as program length, institution type, and location. Understanding these cost components is essential for creating a realistic budget and making informed decisions about financing options.
Understanding Degree Costs

The cost of pursuing a degree is a significant financial consideration for many individuals. It’s essential to understand the various components that contribute to the overall cost, as well as the factors that influence these expenses.
Components of Degree Costs
The total cost of a degree encompasses more than just tuition fees. It includes various expenses that contribute to the overall financial burden.
- Tuition and Fees:This is the primary cost associated with attending a college or university. Tuition covers the cost of instruction, while fees cover administrative services, facilities, and other operational expenses.
- Books and Supplies:Textbooks, course materials, and other essential supplies can add a substantial amount to the overall cost of a degree.
- Living Expenses:This category includes housing, food, transportation, personal expenses, and other living costs. Depending on the location and lifestyle, these expenses can vary significantly.
Typical Degree Costs
The cost of a degree can vary widely depending on the program, institution, and location. Here’s a breakdown of typical costs for various degree programs across different institutions:
- Associate’s Degree:The average cost of an associate’s degree at a public two-year college is around $10,000-$20,000, while private institutions can charge significantly higher fees.
- Bachelor’s Degree:The average cost of a bachelor’s degree at a public four-year university is around $25,000-$40,000. Private universities typically have much higher costs, ranging from $40,000 to $70,000 or more per year.
- Master’s Degree:The cost of a master’s degree can vary widely depending on the program and institution. Public universities generally charge lower fees than private institutions. Master’s programs can range from $20,000 to $60,000 or more.
- Doctoral Degree:Doctoral programs typically involve several years of study and can be very expensive. Public universities generally charge lower fees than private institutions, but the overall cost can still exceed $100,000.
Factors Influencing Degree Costs
Several factors contribute to the variation in degree costs. These include:
- Program Length:Longer programs, such as doctoral degrees, naturally involve higher costs due to extended tuition and living expenses.
- Institution Type:Public institutions generally have lower tuition fees compared to private universities, which often have higher operating costs.
- Location:The cost of living in a particular area can significantly impact degree costs. Cities and metropolitan areas often have higher housing, transportation, and food expenses.
- Program Specialization:Certain specialized programs, such as medical school or law school, can have significantly higher costs due to specific facilities, equipment, and faculty expertise.
Exploring Financing Options
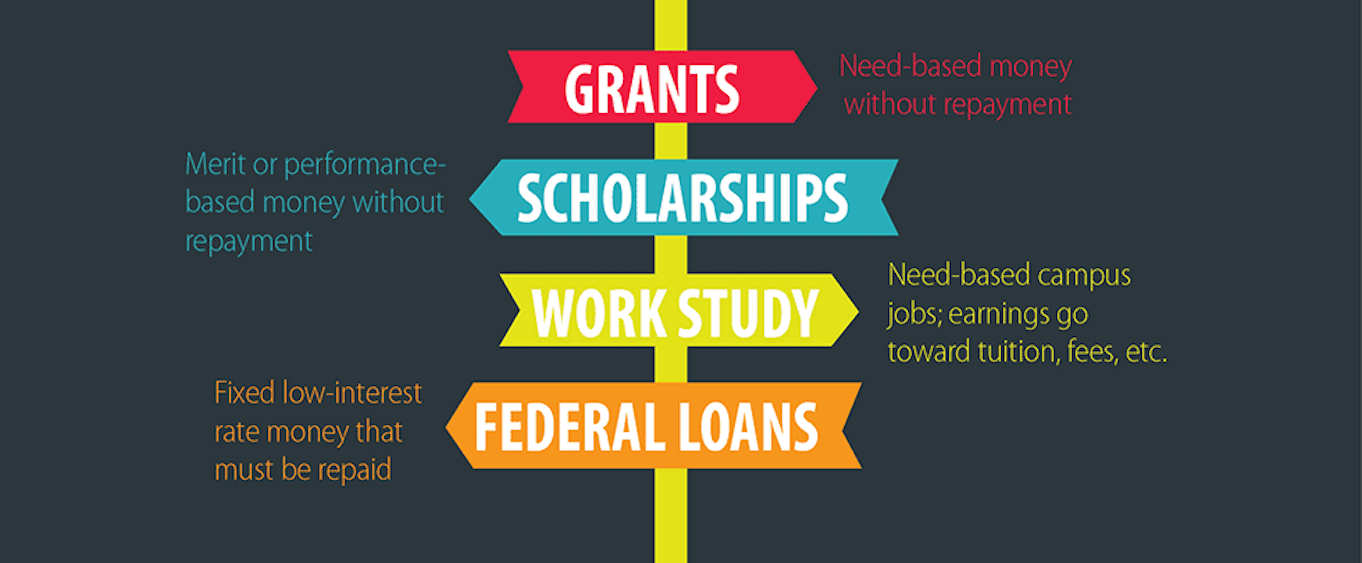
Securing funding for your education is a crucial step in your journey towards achieving your academic goals. Fortunately, a wide range of financing options are available to help you manage the costs associated with pursuing a degree program. This section explores common financing avenues, including scholarships, grants, loans, and work-study programs, providing insights into their eligibility criteria, application processes, and potential impact on your future financial well-being.
Scholarships
Scholarships are a form of financial aid that does not require repayment. They are typically awarded based on academic merit, financial need, or specific criteria such as ethnicity, athletic ability, or community involvement.
- Merit-based scholarshipsrecognize academic excellence, often measured through GPA, standardized test scores, or research accomplishments. These scholarships reward high-achieving students for their academic prowess.
- Need-based scholarshipsconsider a student’s financial circumstances, taking into account factors such as family income, assets, and outstanding debts. These scholarships aim to alleviate the financial burden on students from low-income backgrounds.
- Specific criteria scholarshipstarget students with particular characteristics, such as those belonging to a specific ethnic group, pursuing a particular field of study, or demonstrating leadership qualities.
The application process for scholarships can vary widely. Some scholarships are automatically considered based on your application for admission to the university, while others require separate applications.
The rising cost of college degrees is a major concern for students and families, forcing many to consider student loans and other financing options. Understanding the financial implications of Higher Education is crucial, as the burden of debt can significantly impact future financial stability.
Navigating these costs requires careful planning and consideration of various financing strategies to ensure a sustainable path to higher education.
The key is to thoroughly research available scholarships and tailor your applications to each specific requirement.
Grants
Grants, like scholarships, are forms of financial aid that do not need to be repaid. They are typically awarded based on financial need and are often funded by government agencies, private organizations, or universities themselves.
The rising cost of higher education has prompted many to seek alternative pathways, and distance education has emerged as a compelling option. Distance Education offers flexibility and affordability, often with tuition rates lower than traditional brick-and-mortar institutions. This shift towards online learning has also spurred innovation in financing options, with more scholarships, grants, and income-share agreements becoming available for distance learners.
- Federal Pell Grantsare available to undergraduate students with exceptional financial need. The amount awarded is determined by the student’s Expected Family Contribution (EFC), which reflects their family’s ability to contribute to college costs.
- State grantsare offered by individual states and may have varying eligibility requirements. These grants often target students who are residents of the state and meet specific criteria, such as academic performance or field of study.
- Institutional grantsare awarded by individual universities and colleges. These grants are often based on financial need, academic merit, or specific program requirements.
Grant applications typically require students to submit the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA), which provides a comprehensive overview of their financial circumstances.
Loans
Loans provide temporary financial assistance that must be repaid with interest. They are a common financing option for students, allowing them to cover educational expenses that they cannot afford through other means.
The rising cost of higher education has put a strain on students and their families, leading to increased reliance on student loans. Navigating this complex financial landscape requires understanding the various options available, including federal and private loans, as well as the impact of University Policies on financial aid and tuition.
Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of these factors is crucial for making informed decisions about degree costs and financing.
- Federal student loansare offered by the U.S. Department of Education and are generally considered the most favorable option due to lower interest rates and flexible repayment plans. These loans are typically divided into subsidized and unsubsidized loans, with the former offering interest-free periods while the student is enrolled in school.
- Private student loansare offered by banks, credit unions, and other private lenders. While these loans can provide additional funding, they often come with higher interest rates and less flexible repayment terms. It is crucial to carefully compare interest rates, repayment terms, and fees before taking out private loans.
Loan applications typically require students to provide their credit history, income information, and details about their educational program.
Work-Study Programs
Work-study programs offer students the opportunity to earn income while gaining valuable work experience. These programs are typically funded by the federal government and are available to students with demonstrated financial need.
- Federal Work-Studyallows students to work part-time on campus or at a community organization. The earnings from these jobs can be used to offset educational expenses, providing a practical way to manage costs.
Eligibility for work-study programs is determined based on the student’s financial need and the availability of work-study positions at the university.
Strategies for Managing Degree Costs: Degree Costs And Financing
Navigating the financial landscape of higher education requires a proactive approach. While the cost of a degree can be daunting, several strategies can help students manage expenses effectively and minimize the financial burden. By understanding and implementing these strategies, students can pave the way for a financially sound educational journey.
Creating a Realistic Budget, Degree Costs and Financing
A well-structured budget is essential for managing degree costs effectively. This involves carefully assessing income sources and potential expenses.
- Identify Income Sources:Begin by listing all potential income sources, including scholarships, grants, loans, part-time jobs, and any financial assistance from family or friends.
- Estimate Expenses:Create a comprehensive list of anticipated expenses, including tuition and fees, books and supplies, housing, food, transportation, and personal expenses.
- Track Spending:Regularly monitor your spending habits to ensure you stay within your budget. Utilize budgeting apps or spreadsheets to track your income and expenses effectively.
- Adjust as Needed:Life is unpredictable, and your financial situation may change over time. Be prepared to adjust your budget accordingly to accommodate unexpected expenses or changes in income.
Minimizing Degree Costs
Several strategies can help students minimize the overall cost of their degree program.
- Explore Scholarships and Grants:Scholarships and grants are forms of financial aid that do not require repayment. Explore various scholarship databases, websites, and organizations to identify opportunities that align with your academic profile, interests, and background.
- Maximize Financial Aid:Federal and state financial aid programs can provide significant assistance. Complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) to determine your eligibility for grants, loans, and work-study programs.
- Reduce Living Expenses:Consider affordable housing options, such as living with family, roommates, or in student housing. Explore cost-effective meal plans and grocery shopping strategies to manage food expenses.
- Take Advantage of Free Resources:Many universities offer free resources, such as tutoring, career counseling, and academic advising, which can save students money on external services.
- Negotiate Costs:Inquire about potential discounts on tuition, fees, or other expenses. Some universities may offer discounts for early registration, payment in full, or for students who demonstrate financial need.
Managing Finances Effectively
Managing finances effectively throughout your degree program is crucial.
- Utilize Online Banking:Online banking platforms allow you to track transactions, set up automatic payments, and manage your accounts from anywhere.
- Budgeting Apps:Various budgeting apps are available to help you track expenses, create budgets, and set financial goals.
- Financial Literacy Resources:Seek out resources that provide information on personal finance, credit management, and investing.
- Seek Professional Advice:If you are struggling to manage your finances, consider seeking professional advice from a financial advisor or counselor.
Long-Term Financial Implications

Student loan debt can significantly impact your financial future, influencing major life decisions like buying a home, saving for retirement, and investing. Understanding the long-term implications of student loans is crucial for navigating your financial journey effectively.
Impact on Financial Planning
Student loan debt can significantly influence your financial planning, impacting your ability to reach important financial goals.
- Homeownership:High student loan payments can reduce your affordability for a mortgage, making homeownership a more challenging goal. The amount of debt you carry can affect your debt-to-income ratio (DTI), a key factor lenders consider when assessing your mortgage eligibility.
- Retirement Savings:Significant student loan payments can limit your ability to contribute to retirement savings, impacting your financial security in later years. With a substantial portion of your income dedicated to debt repayment, you may have less disposable income to invest for retirement.
- Investment Opportunities:Student loan debt can also restrict your ability to invest in other assets, such as stocks or mutual funds, limiting your potential for wealth accumulation. Your focus on repaying student loans may reduce your capacity to take advantage of investment opportunities that could contribute to long-term financial growth.
Strategies for Managing Student Loan Debt
Managing student loan debt effectively is crucial for achieving financial stability and pursuing long-term goals.
- Repayment Options:Explore different repayment options available, such as income-driven repayment plans, which adjust your monthly payments based on your income. This can help make your payments more manageable, especially during periods of lower income.
- Consolidation:Consolidating your student loans into a single loan with a lower interest rate can reduce your overall interest payments and monthly payments. This can make your debt more manageable and help you pay it off faster.
- Refinancing:Refinancing your student loans with a private lender can potentially secure a lower interest rate, leading to lower monthly payments and faster debt repayment. However, it’s essential to consider the terms and conditions of private loans carefully before refinancing.
Building a Strong Financial Foundation
Graduating with student loan debt can be challenging, but establishing a solid financial foundation is crucial for long-term financial success.
- Income Generation:Focus on maximizing your income potential by seeking high-paying jobs or pursuing career advancements. This will provide you with more resources to manage your student loan payments and achieve other financial goals.
- Debt Management:Prioritize managing your student loan debt by making timely payments and exploring repayment options that fit your financial situation. This demonstrates responsible financial behavior and can help you avoid penalties and negative impacts on your credit score.
- Savings Strategies:Develop a savings plan and prioritize building an emergency fund. Having a financial cushion can provide you with security and flexibility to navigate unexpected expenses and financial challenges.
Final Wrap-Up
Navigating the complexities of degree costs and financing requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding the costs involved, exploring diverse financing options, and implementing strategic management techniques, individuals can mitigate the financial burden of higher education and pave the way for a brighter future.
Remember, a well-informed approach to managing degree costs can empower you to achieve your educational goals while maintaining financial stability.
